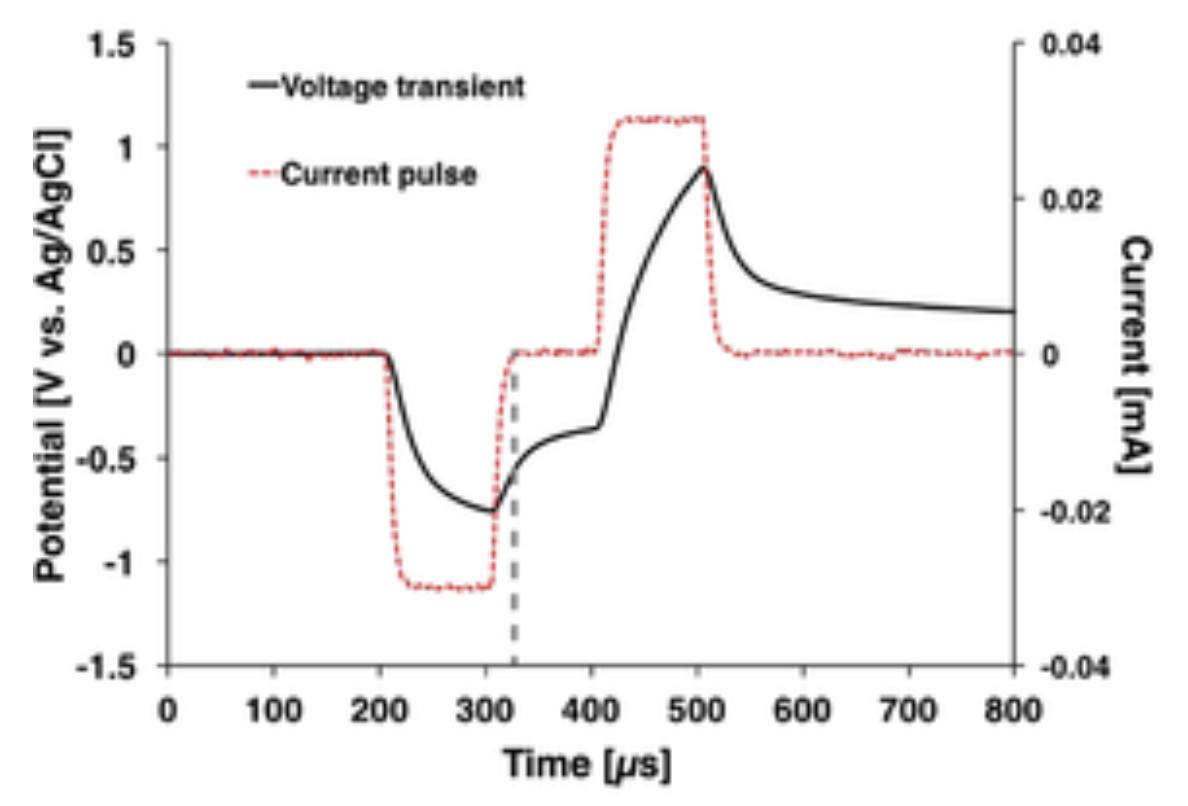
A voltage transient is a brief, temporary changes in the electrical potential (voltage) of a neuron’s membrane, often caused by synaptic activity or other stimuli
Caused by:
- Synaptic inputs: The arrival of neurotransmitters at synapses can cause either depolarization (making the membrane potential more positive) or hyperpolarization (making it more negative).
- Action potentials: The rapid depolarization and repolarization that characterize action potentials are also voltage transients.
- Other stimuli: Electrical stimulation, sensory inputs, or even certain internal processes can induce voltage transients.