Engram and Memory Allocation/Encoding
Overview
In neuroscience, an engram is the physical substrate of a memory, essentially a “memory trace” in the brain. It represents the changes in neural circuits that occur when a memory is formed, stored, and later retrieved. Understanding engrams is crucial for deciphering how memories are allocated and encoded in the brain, which has profound implications for both neuroscience and artificial intelligence (AI).
Key Concepts
- Memory Trace: The specific neurons and synaptic connections that are altered during the encoding of a memory, believed to form the engram.
- Encoding: The process by which perceived information is transformed into a construct that can be stored in the brain, involving changes in synaptic strength and neural activity.
- Memory Allocation: Refers to how certain neurons and circuits are selected and modified to store a particular memory.
Neural Mechanisms
Synaptic Plasticity
- Long-Term Potentiation (LTP): A process where the strength of synapses (connections between neurons) is increased, making it easier for neurons to communicate in the future. LTP is considered a key mechanism underlying memory formation.
- Long-Term Depression (LTD): The weakening of synaptic connections, which can also be involved in encoding memories, especially in processes like forgetting or memory refinement.
Neuronal Ensembles
- Cell Assembly: A concept proposed by Donald Hebb, suggesting that memories are stored in networks of neurons that become functionally connected when activated simultaneously during an experience.
- Tagging and Capture: The idea that specific neurons are “tagged” during a memory encoding event, and these tags attract the molecular changes needed to solidify the memory trace.
Memory Allocation and Retrieval
Selectivity in Neurons
- Not all neurons are involved in every memory; instead, specific neurons are allocated to store a particular memory based on factors like their pre-existing activity levels, connectivity, and intrinsic properties.
- Neuronal Competition: During memory allocation, neurons may compete based on their excitability and connectivity, with the most active neurons more likely to be recruited into the memory trace.
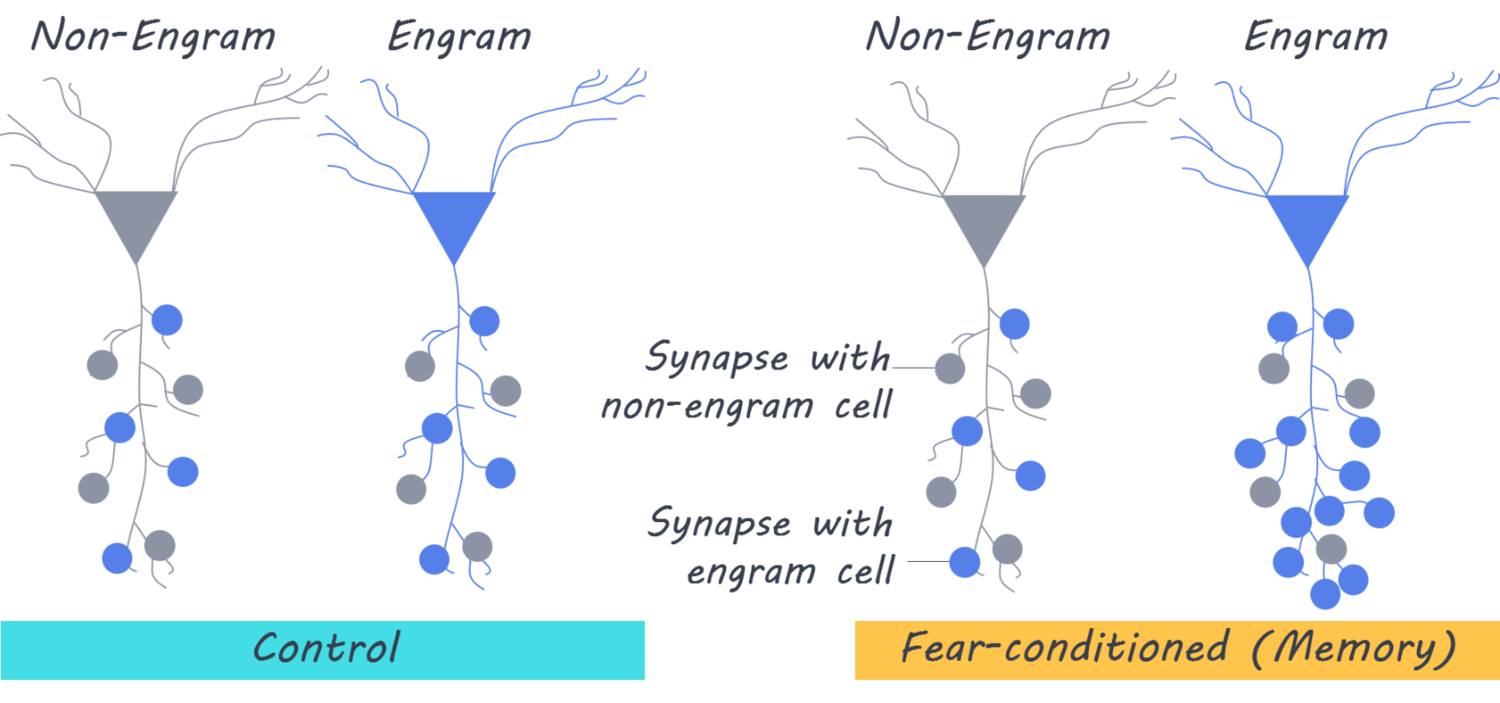
Engram Cells and Reactivation
- Engram Cells: Specific neurons that have been altered to store a memory. Reactivating these cells (e.g., through optogenetic techniques in experimental settings) can lead to the recall of the associated memory, even in the absence of natural cues.
- Pattern Completion: The process by which a partial or degraded cue can reactivate the full memory by stimulating the corresponding engram cells, a concept that is also explored in AI for memory reconstruction tasks.
Implications for AI
Neural Networks and Memory
- Memory Networks: The concept of engrams and memory allocation in the brain can inspire more efficient memory storage and retrieval mechanisms in artificial neural networks, particularly in models designed for tasks like sequential learning and pattern recognition.
- Plasticity in AI: Incorporating principles of synaptic plasticity into AI models could lead to more adaptive learning systems that can dynamically reallocate resources as new information is encoded.
AI and Neuroscience Interface
- Biologically Inspired Models: Engrams provide a framework for creating more brain-like memory systems in AI, with the potential for models that better mimic human memory processes, such as context-dependent recall and pattern completion.
- Understanding Forgetting: Insights from engram research can help develop AI systems that not only learn new information but also manage forgetting in a way that optimizes performance, similar to how the brain refines and prioritizes memories over time.
Further Reading
- Synaptic Plasticity: Delve deeper into how LTP and LTD contribute to the formation of engrams.
- Memory Reconsolidation: Explore how memories can be modified and updated, providing insight into both human cognition and potential AI applications.
- Optogenetics and Engrams: Learn about experimental techniques used to manipulate and study engrams in live organisms, offering parallels to manipulating memory in AI models.
- Engram Memory Video