The medial septum is a brain structure that is located in the Basal Forebrain, near the midline of the brain
Structure
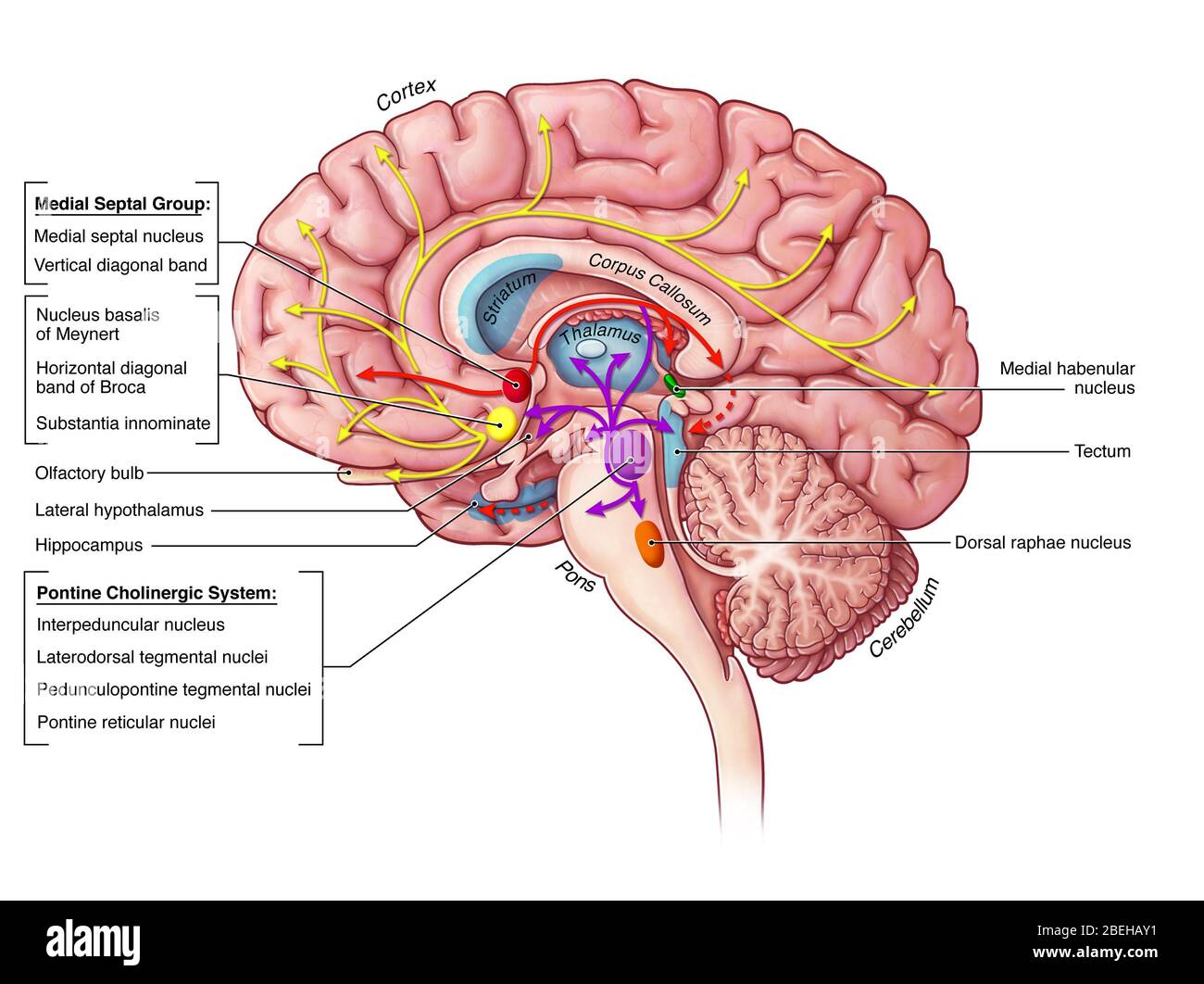
The medial septum itself consists of a few sub parts, namely the Medial Septum Nucleus, Diagonal Band of Broca, and the Lateral Septum
In terms of the Basal Forebrain, the medial septum is a part of the septal nuclei.
Medial Septum Nucleus
The medial septum nucleaus (MSN) plays a crucial part in the formation of theta waves in the Hippocampus.
More specifically, GABAergic cells of the medial septum that act as theta pacemakers target dentate gyrus, CA3, and CA1 interneurons. Pacemaking MS interneurons express hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) channels which likely, at least partially, mediate their pacemaker properties.1
Essentially, think of the medial septum nucleus as the conductor of the orchestra that is the hippocampus.
Diagonal Band of Broca
The diagonal band of Broca is a structure that is located in the basal forebrain, and is a part of the medial septum. For the medial septum, it is involved in the regulation of the Hippocampus.
Lateral Septum
For the medial septum, the lateral septum is a structure that is located in the Basal Forebrain, and is involved in the regulation of the Amygdala.
Purpose
The medial septum plays quite the broad role in the brain, but it is mostly involved the process of memory formation and regulation. This consists of working with the Hippocampus and the Amygdala to regulate the formation of memories and the regulation of emotions.
But more specifically, the medial setpum is responsible for the construction of spatial maps in the brain, which are crucial for the formation of memories. this involves generating theta waves in the hippocampus, which are the primary brain waves that are associated with memory formation.
Beyond that, the medial septum also plays a roll in social and emotional behaviors, namely in the regulation of aggression and anxiety.