Boltzmann Machine Neural Network
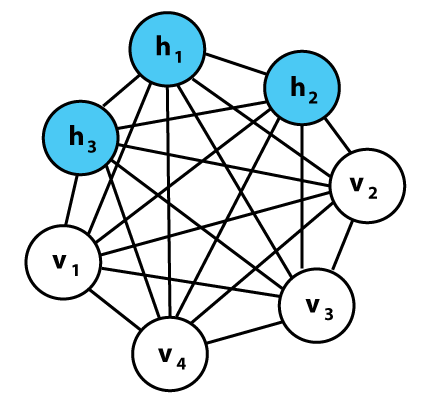
Overview
A Boltzmann Machine is a type of stochastic (randomly determined) neural network that is used to model probability distributions over binary-valued patterns. It’s a foundational model in the field of probabilistic graphical models and deep learning. It is named after the Boltzmann distribution in statistical mechanics.
The Boltzmann Machien is an evolution of the ideas presented by the memory modelling Hopfield Networks. By just adding the two important concepts of stochastically and hidden units, just about any Hopfield Network can be transformed into a Boltzmann Machine
Key Components
- Neurons: The basic units of a Boltzmann Machine, which are typically binary, meaning they can take on a value of either 0 or 1.
- Weights: Connections between neurons have weights, which determine the strength and direction of their interaction.
- Energy Function: The state of the network is characterized by an energy function, which the network seeks to minimize.
Probability and Uncertainty
Energy and Probability
- The probability of a certain state in the Boltzmann Machine is related to its energy by the Boltzmann distribution:
where ( E(\text{state}) ) is the energy of the state, and ( Z ) is the partition function, which normalizes the probabilities.
- Lower Energy States: States with lower energy are more probable. The learning process involves adjusting the weights to lower the energy of desired states, making them more likely.
Uncertainty and Stochastic Behavior
- Unlike traditional deterministic neural networks, the stochastic nature of Boltzmann Machines introduces uncertainty in the output. Each neuron has a probability of being on or off, which is not fixed but instead influenced by the state of other neurons and their connection weights.
- Annealing: A technique inspired by statistical mechanics, where the “temperature” is gradually reduced during training to help the network settle into a state of minimal energy, thereby finding a good solution amidst uncertainty.
Learning in Boltzmann Machines
- Contrastive Divergence: A commonly used learning algorithm that approximates the gradient of the log-likelihood of the data.
- Sampling: During learning, the machine needs to sample from the distribution it is modeling, which can be computationally intensive, especially for large networks.
Applications and Significance
- Deep Learning: Boltzmann Machines, especially the Restricted Boltzmann Machine (RBM) variant, are key building blocks in the development of deep learning architectures such as Deep Belief Networks (DBNs).
- Understanding Probability: The Boltzmann Machine has contributed significantly to the understanding of how probability and uncertainty can be modeled and leveraged in neural networks. It allows for the representation of complex probability distributions and captures the inherent uncertainty in many real-world problems.
Further Reading
- Deep Belief Networks (DBNs): Understand how RBMs are stacked to form DBNs.
- Gibbs Sampling: Learn about the method often used for sampling from the Boltzmann distribution.
- Statistical Mechanics: Explore the roots of the Boltzmann distribution in physics, which underpins the theoretical foundation of Boltzmann Machines.
- Boltzmann Machine Video